Pediatric Tui Na

Vomiting is a common symptom in children and can be seen in various diseases. The causes can be attributed to food stagnation, accumulation of heat in the stomach, or weakness of the spleen and stom

If a child has poor spleen and stomach function, it can cause food accumulation and even vomiting. Vomiting is a common digestive symptom. Let's take a look at the massage techniques for treating foo

Cough is a common symptom of respiratory diseases. It can occur due to external factors or internal imbalances in lung function. Coughing is most commonly seen in infants and young children under th

Cough can occur in various respiratory and lung diseases, such as colds and pneumonia. It can occur all year round, but is most common in winter and spring. There are two types of cough: external an

Pediatric spleen and stomach are weak, easily damaged by milk, cold food, and accumulated heat, resulting in spleen deficiency and inability to transform water and grains into essence. Instead, it p

Cough caused by internal organ damage is known as internal organ cough, including phlegm-heat cough, phlegm-damp cough, yin deficiency dry thirst cough, and lung deficiency cough. Now let's take a l
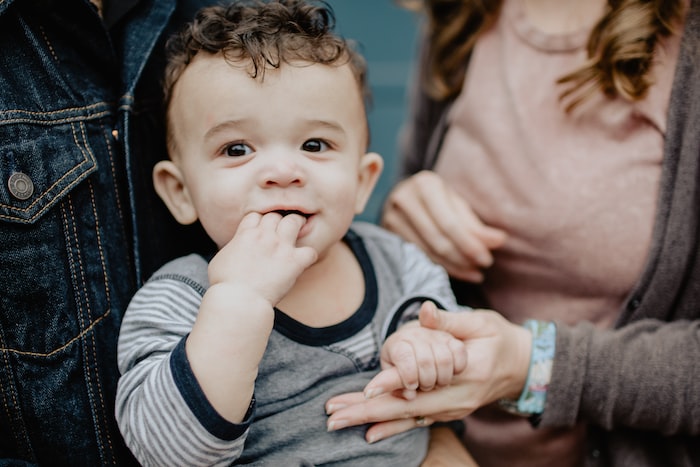

Pediatric fever is a common condition, which can be a standalone disease or caused by various illnesses. Some babies may even experience fever as a result of being startled. Many parents prefer to use

Fever, as a symptom, can occur in various acute and chronic diseases, regardless of external or internal causes. Children, especially those with weak immunity, are more prone to fever due to their v

Ganji in gan refers to the imbalance of diet in children, improper feeding, weak spleen and stomach, incomplete digestion and absorption, characterized by slow disease progression, thin body, dull h
Mumps is an acute infectious disease caused by external pathogenic wind-heat toxins, which block the Shaoyang meridian and accumulate in the cheeks. Its clinical features include fever and diffuse s